The need to develop data skills as part of digital equity programs
Digital equity is key to empowering everyone to interact confidently in today’s digital world. Our blog explains the importance of data skills to digital inclusion - and how organizations can help drive data democratization.

In an increasingly digital world, ensuring everyone has the ability to access and harness the internet is vital across society. It gives everyone the ability to interact digitally in their work and home lives, whatever their background or location.
That’s why the US federal government has committed $65 billion to roll out high speed broadband infrastructure across all 50 states as part of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA).
Creating digital equity and inclusion
However, installing technology alone is not enough. As Amy Huffman, policy director for the National Digital Inclusion Alliance (NDIA) explains in this interview with GovTech, “You can’t close the digital divide with just pipes and wires. You have to also address the human side of the equation.”
So the federal government has earmarked $2.75 billion of funding to invest in digital equity programs, under the Digital Equity Act (DEA). At a state level these aim to deliver the skills and devices that everyone requires to benefit from digital technology, from navigating the internet with confidence to interacting digitally with government, businesses, friends and colleagues. Digital equity programs will bring together stakeholders from the government, voluntary and private sectors to engage with and empower citizens.
Becoming data citizens
As digital equity plans and training programs are created, it is vital not to forget the importance of data skills to digital inclusion. As Olivier Thereaux of the Open Data Institute explains in this blog, it is vital everyone is able to confidently use data in their home and working lives.
Increasing data skills provides benefits in seven key areas:
For citizens:
- It helps people make better decisions based on data, rather than hunches, delivering better results
- It ensures people can properly understand the information they are accessing, enabling them to spot potential attempts to misinform or defraud them
- It helps individuals better protect their data and safeguard their rights, such as by ensuring they do not provide unnecessary access to confidential information
- It helps consumers change their own behavior, such as around energy/resource use by analyzing consumption data and making more sustainable choices
For organizations and communities:
- It increases transparency for government agencies, municipalities and cities by allowing citizens to hold them accountable through the open data that they publish on their performance
- It increases accountability for private sector organizations, enabling consumers to understand their activities (such as around ESG/CSR commitments) and monitor their progress towards them
- It enables closer collaboration within communities, with groups working together through shared data to solve societal problems in their neighborhoods and beyond
Data skills should include being able to understand what type of data is being provided (such as quantitative or qualitative), the source/how it was collected, the quality of the data, who has shared it, any potential bias within the source, and the metrics used in order to be able to make meaningful comparisons between different datasets.
Building data skills - how the public and private sector can help
Providers of data, whether municipalities, businesses or state governments can support the development of data skills in a number of ways:
Share relevant data via open data portals
The aim should be to publish all data that could be of interest, provided it is not confidential or allows people to be personally identified. The more data is available, the greater the opportunities for people to create value from it.
The North Carolina Office of State Budget and Management (OSBM)’s LINC open data portal aims to provide a one stop shop for data about the state. It brings together a wide range of datasets, covering areas as diverse as population (including census data), labor force, education and agriculture. Users range from government officials to school children completing projects and those looking to move to the state.
Make data inviting and easy to access
Even with data skills in place, organizations shouldn’t expect users to be data experts. They need to democratize their data by making it as inviting and accessible as possible. This means going beyond simply providing raw data to focusing on visualizations that explain the data and make it easily digestible.
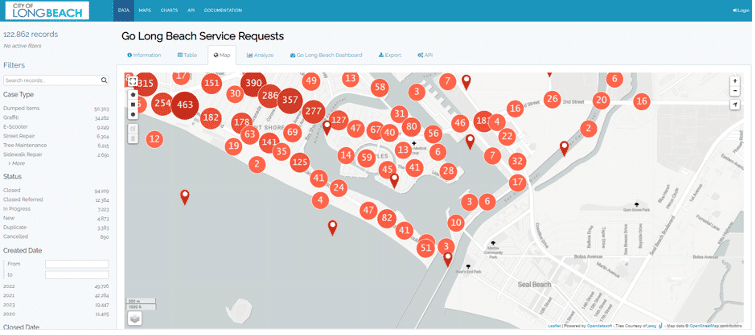
Every dataset on the City of Long Beach’s open data portal contains interactive dashboards showing the data visually, ensuring it is appealing and understandable at a glance. For example, its Go Long Beach Service Requests dataset shares information on all service requests received through the city’s 311 app, covering areas such as incidents of graffiti, potholes or dumped items. Displayed via an interactive map, users can see local incidents as well as look at trends, such as time to closure, in order to highlight areas for improvement.
Make it searchable and reusable
Data portals can contain hundreds of datasets with thousands of data points. It is therefore vital it is as easy as possible for users to find the data they are looking for – and when they have found it they are confident in what it contains. This requires clear metadata tagging of every dataset, with terms everyone will understand, rather than industry acronyms or jargon. Equally data has to be easy to reuse – people have to be able to download it in common formats and use APIs to automatically incorporate it into their own apps and solutions.
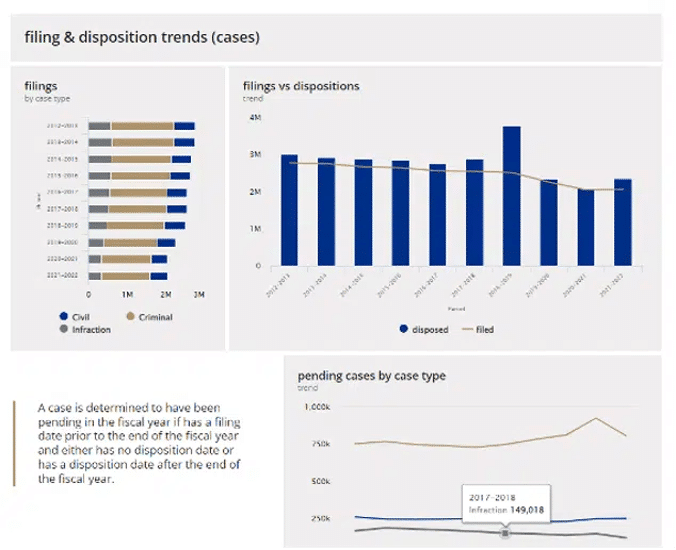
North Carolina Administrative Office of the Courts (NCAOC) aims to increase accessibility and transparency around the justice system in the state. Its open data portal not only delivers access to raw data and visualizations around caseloads but ensures that all information is clearly explained for non-legal specialists, increasing understanding.
Focus on the right datasets
Organizations need to provide as much data as they can, particularly when it comes to public sector transparency. However, it is important to go beyond the basics and engage users with data that focuses on their interests and needs. Conduct feedback with users to find out what they’d like to see and monitor which data is used most so more can be added on similar subjects.
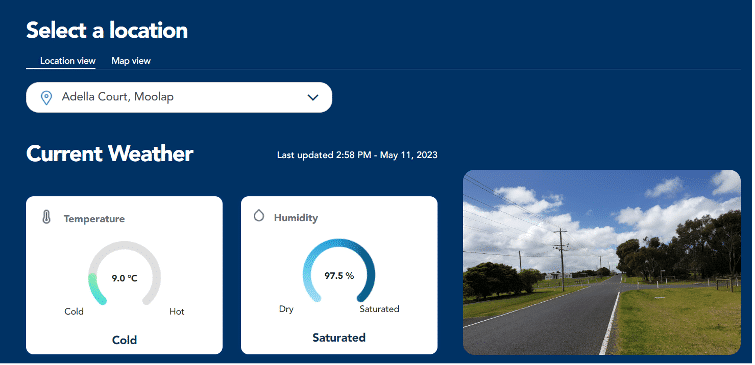
The City of Geelong in Australia’s Weather Together project recruited volunteers to host weather sensors in their home or workplace. Involving the community provides a real-time picture of temperature and weather across the city, while encouraging people to get involved and access the data in their day-to-day lives, driving data democratization.
Digital equity is key to ensuring that everyone has the skills, access and confidence to make the most of digital opportunities. Given the enormous and growing role data plays in our digital world, ensuring everyone has the right data skills is a vital part of ensuring digital equity for all.



