Building sustainability and the circular economy through data portals
Data is critical to creating a more sustainable and greener society, particularly when it comes to building circular economies that reuse materials that would otherwise go to landfill. Read our blog to find out why data portals are essential to the data sharing that underpins circular economies.

Across industries and countries, there’s a pressing need to become more sustainable in everything we do. Embracing circular economies by reusing materials and products is a crucial part of building this greener future. It reduces wastes and safeguards often scarce resources as circular economies minimize the need to manufacture new products from scratch.
However, building circular economies requires collaboration across sectors and ecosystems, often between non-traditional partners who do not normally work together. Data sharing is essential to underpin this collaboration. Data needs to be used to track products and their individual components and then inform the wider ecosystem about their availability and location. This ensures that products and resources can be easily accessed and reused, with all the sustainability benefits this delivers.
Data portals provide the perfect way to share data across circular economies, acting as a one-stop-shop for all relevant information so that it can be easily accessed by everyone across the ecosystem, and then reused to drive greater collaboration. Data can be visualized in understandable, engaging ways, such as through interactive maps and dashboards, or downloaded automatically via APIs or common file formats to feed into technology systems and tools.
Introducing the circular economy
What is the circular economy?
The concept of reusing materials and reducing waste in a closed-loop or circular economy was first championed in the 1970s by Dr. Walter Stahel. Since then it has been developed, particularly through government regulations that make companies responsible for dealing with the entire lifecycle of their products. For example, the EU’s forthcoming Digital Product Passports will help build circular economies by making it mandatory to provide detailed information on products and their components, aiding reuse.
The circular economy is now seen as a key pillar of achieving Net Zero objectives and boosting sustainability, alongside increasing energy efficiency and reducing emissions. Many companies, such as H&M and Zara, have committed to transforming themselves to be part of the circular economy, collecting and reusing old products (such as clothes) as part of their operations.
What are the benefits of the circular economy?
The circular economy delivers four key benefits to producers, customers and the wider environment:
- It minimizes waste. Old or obsolete items are not sent to landfill, but instead are repurposed or their materials reused in new products.
- It reduces emissions. In many cases, the manufacturing process creates significant carbon emissions. As fewer new products are created due to reuse, emissions are lowered.
- It safeguards resources. Valuable commodities (such as the rare metals used within EV batteries) can be extracted from products and then reused in new ones. This reduces the need to expensively mine new materials, lowering the impact on the environment.
- It opens up new revenue opportunities. Materials that companies previously had to pay to dispose of to landfill can now be sold to companies that want to reuse them.
How data portals overcome the challenges to building the circular economy
The importance of data in the circular economy
Today’s economies produce enormous amounts of waste, which traditionally went to landfill. Now, it is increasingly being collected and sorted into different waste streams that can be reused within circular, closed-loop economies. This makes data sharing vital to:
- Show what a particular product contains in terms of raw materials, so that they can be extracted and reused
- Track the carbon footprint of a product, and to use this information to meet regulatory requirements and show the sustainability improvements that reuse brings
- Show where materials and products are located, and their quantities, so that they can be accessed and incorporated into circular economy ecosystems
Bringing together new ecosystems
The circular economy cuts across sectors and brings together public and private sector players in new ecosystems. Data acts as a bridge between organizations, helping them collaborate across the product lifecycle. For example, plastic waste collected by municipalities or private companies may be supplied to manufacturers that turn it into pellets. These can then be used by a range of different companies in different sectors to make completely new products, such as park benches, car components or building materials.
However, for ecosystems to form, they need to be able to connect suppliers and producers, especially at a local level. To invest in using recycled materials, companies have to be sure that they will have access to sufficient supplies, now and in the future. That means data has to be predictive, able to show which resources will be available, when and in what quantities.
The role of data portals in the circular economy
Data portals play a critical role in connecting the ecosystem. They provide a central place for the seamless sharing of up-to-date, reliable information with everyone across the ecosystem. As they are web-based, everyone can access them without requiring specific technology or tools, and given that they are intuitive, there’s no need to provide specialist training for users. Information is available in a range of formats to meet different needs – as raw data, through visualizations such as maps and dashboards or downloadable through APIs or standard formats.
Whether hosted by one player in the ecosystem or through an neutral organization, data portals enable collaboration between different companies, many of whom may not traditionally partner with each other. They increase efficiency as data is automatically available, without requiring expensive integrations between company IT systems and they can be used predictively to model future scenarios and drive investment decisions. Portals also have a vital role to play in delivering transparency to stakeholders, including regulators, consumers and investors, showing how companies are embracing reuse and the circular economy.
Data portals and the circular economy - best practice examples
Organizations across the globe are increasingly using data portals to drive their circular economy efforts, including Opendatasoft customers around the world. These include:
Western Sydney Circular Economy Innovation Challenge
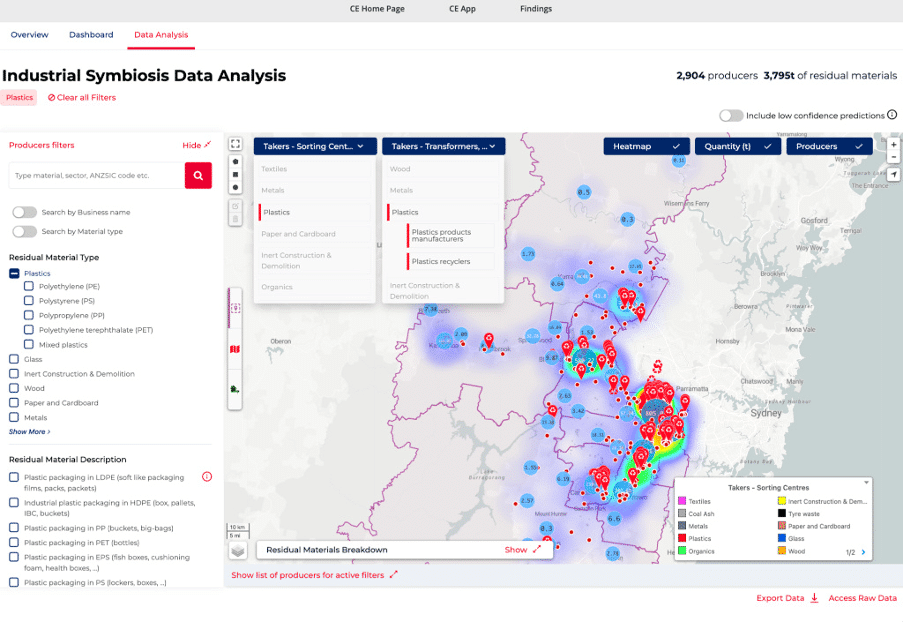
Winner of the New South Wales Government 2022 Circular Economy innovation challenge, this new Australian project is being deployed across eight local government areas in Western Sydney. It is designed to predict the waste produced by more than 20,000 businesses across 200+ industry sectors in the region, and to make this information easily available to all via a data portal. Detailed data is organized into over 100 material types covering wood, organics, plastics, metals, construction & demolition, paper and cardboard, glass and textiles.
With the data, local and state government can now assess investment opportunities at a strategic level for new infrastructure to meet circular economy needs. Data also feeds into a local online material exchange marketplace where local businesses can connect and trade materials, opening up new revenue streams. While not yet live, the project will be part of the existing Western Parkland Councils open data site, which also features data from an extensive sensor network to monitor sustainability across the region.
Sustainable Ajman
The Emirate of Ajman, one of the seven emirates that make up the United Arab Emirates (UAE), includes a focus on the circular economy on its open data portal. Its Sustainable Ajman initiative provides a hub for sustainability, sharing data about all types and volumes of waste produced across the emirate. Delivered through a combination of raw data, data stories, interactive maps and dashboards, it has been created by a collaboration between the Municipality & Planning Department and Digital Ajman.
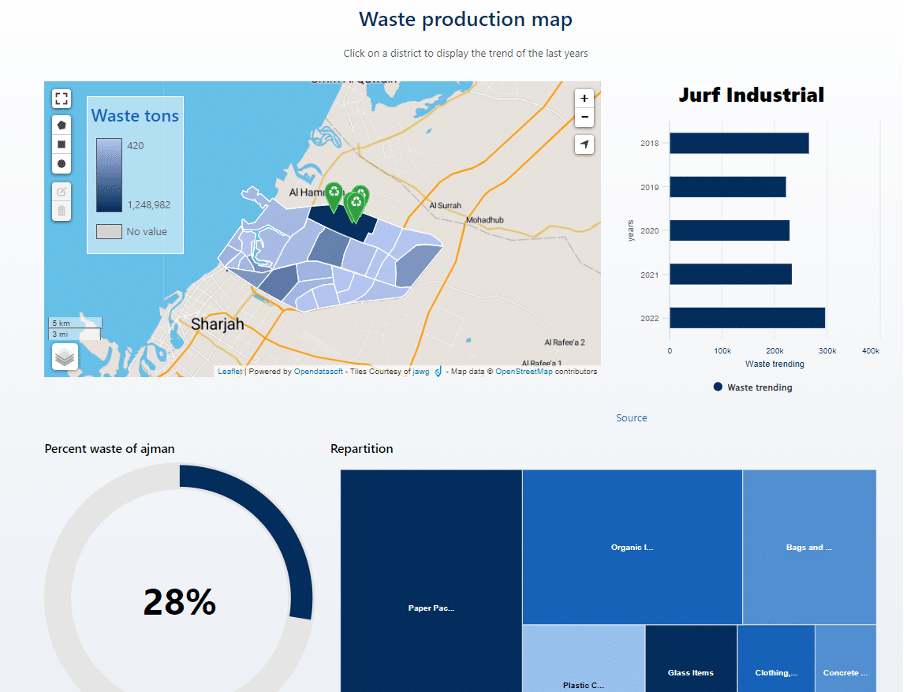
It encourages citizens to recycle more and highlights the facilities that have been put in place to make Ajman more sustainable. For example, it showcases initiatives including:
- How paper and plastic waste from Ajman Municipality buildings are being collected and turned into environmentally-friendly products such as fiber-based clothes for orphaned children.
- How wood waste from the carpentry industry/used furniture is now used by paper and pallet manufacturers, rather than going to landfill
Conclusion - why you need a data portal for the circular economy
The world faces a pressing need to reuse increasingly scarce resources – a goal that circular economies help meet. Building these collaborative, symbiotic circular economies relies on data sharing to provide a full picture of resources, now and in the future, as well as monitoring company progress against circularity objectives. Data portals are therefore vital in bringing together ecosystems, and enabling circular economies to improve sustainability and reduce carbon emissions.