The growing importance of open data in the Middle East
How can open data underpin digital transformation across the Middle East, and what are the challenges to its adoption? We look at the benefits open data brings, illustrated with best practice examples from our customers.

Increasing the use of data has the potential to transform the economies and societies of the Middle East, and is a key part of digital transformation in the region.
Opening and sharing data is central to this, offering the ability to improve efficiency, increase transparency, and introduce new services for the region’s 400+ million citizens and businesses. This article looks at the state of open data use in the Middle East and current initiatives and best practices that aim to accelerate data sharing.
The current picture of open data in the Middle East
Clearly the Middle East is made up of a diverse range of countries, and this reflects in progress around open data, with some further ahead than others. However, international benchmarks such as the 2022 Global Data Barometer and the Open Data Barometer all show that the region is still at an early stage of its open data journey.
For example, in the Global Data Barometer Saudi Arabia scored the highest at 29%, followed by the United Arab Emirates (27%) and Qatar and Bahrain (both 22%). Oman scored the lowest at 14%. As Riyadh Al-Balushi of Open Data Oman explains in his blog, the Middle East in general scored the lowest among all other regions.
This shouldn’t overshadow the progress that has already been achieved – most countries have made data and digital technologies a key pillar of their future strategies and visions, and have introduced regulations and standards to encourage data sharing. The potential benefits are enormous – for example, advancing digital maturity across the Gulf economies alone represents a $255 billion market opportunity, according to research.
What are the drivers behind open data in the Middle East?
As with other regions, there are a range of drivers that are accelerating the need to open data across the Middle East, including:
Expectations from society
Citizens around the world are now more digitally-literate and interested in data. This is equally true amongst the population of the Middle East. 67% have become more digital since the pandemic, according to research from PwC. They increasingly want the ability to access and analyze open data in their daily lives and interactions.
Expectations from business
Many businesses across the region have invested heavily in big data, analytics and other digitization strategies. Not only do they want to share their data, but they want to be able to harness open, public data to innovate and deliver better services to their customers. For example, the Saudi Central Bank has created an open data portal to share information with its stakeholders and financial specialists. Areas as diverse as energy and mobility all see the benefits in incorporating and sharing open data to drive optimization of their services and launch new customer-focused apps and services.
A desire for transparency
Middle Eastern economies are diversifying away from traditional revenue sources such as oil and gas to embrace new areas such as tourism and advanced technologies such as the metaverse and autonomous robotaxis. To attract both businesses and tourists they understand that they need to be transparent, projecting an open, innovative image. Sharing information about facilities, government activities and smart city initiatives is central to underpinning transparent, future-focused economies.
A focus on monetizing data
Sharing data enables government organizations to meet the changing needs of their business and citizen stakeholders. It also offer the ability to create new revenues, particularly through data services that combine internal and external datasets to optimize them for the requirements of businesses. Supporting this, new regulations have come into force in the UAE to allow the selling of data in this way.
What do Middle Eastern countries need to do?
As international benchmarks demonstrate, Middle Eastern countries need to accelerate their efforts around open data if they are to deliver the benefits of data sharing. Achieving this requires a focus on three areas:
Putting the foundations in place
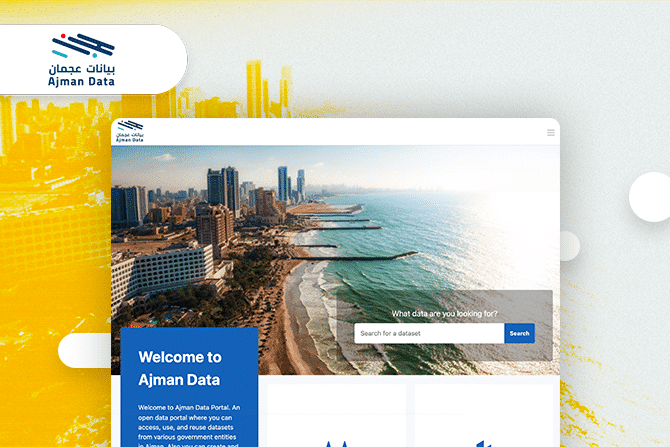
There is a lot of excitement about the potential of new innovations across the region, from advances in sustainability and self-driving cars to the metaverse. These all rely on data, but in many cases the foundations for data gathering and sharing are not yet fully in place. While government departments might be opening their own data, this is not being made available more widely, such as through country-wide data portals. This is changing – for example the Emirate of Ajman has just launched Ajman Data, a portal that brings together data from agencies as varied as the police, tourism and port departments.
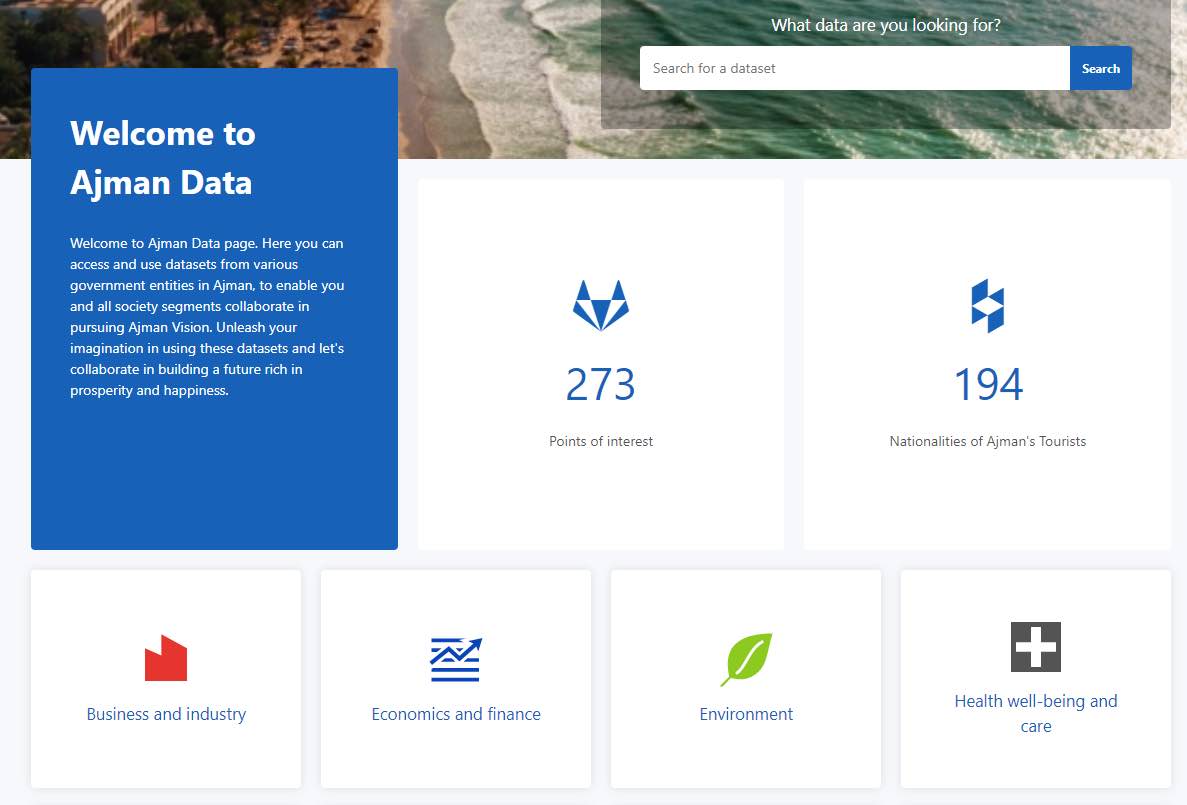
Engaging users with data
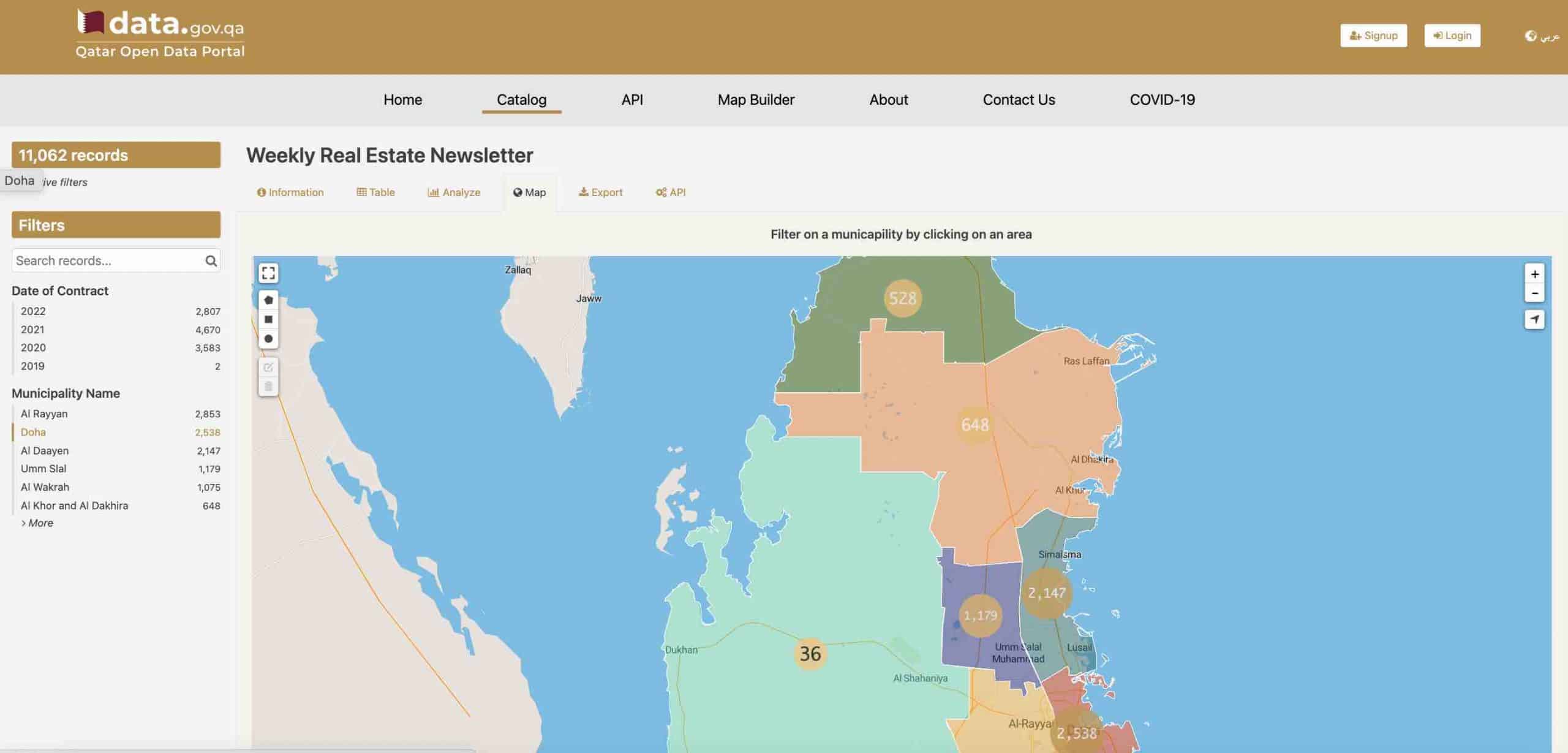
For open data to be used it has to be accessible, understandable and delivered through compelling data experiences that meet people’s needs. That means going beyond simply providing data catalogs to making them searchable, easy to integrate with external apps through APIs, and simple to understand through data visualizations such as maps, charts and data stories. For example, the Qatar Open Data Portal publishes a weekly newsletter of real estate transactions in the country, filterable by municipality.
Creating data cultures within departments
Globally, data has traditionally been concentrated in the hands of experts, such as data analysts and data scientists. Freeing this data and making it available to all is key to data democratization and making better, data-driven decisions. In the Middle East, as in other regions, increasing data sharing isn’t just about implementing new, user-friendly, technology that doesn’t require special skills. Instead, it is about building data cultures where everyone is confident in sharing and using data within their working lives. This culture change is vital to breaking down barriers between departments and delivering data democratization.
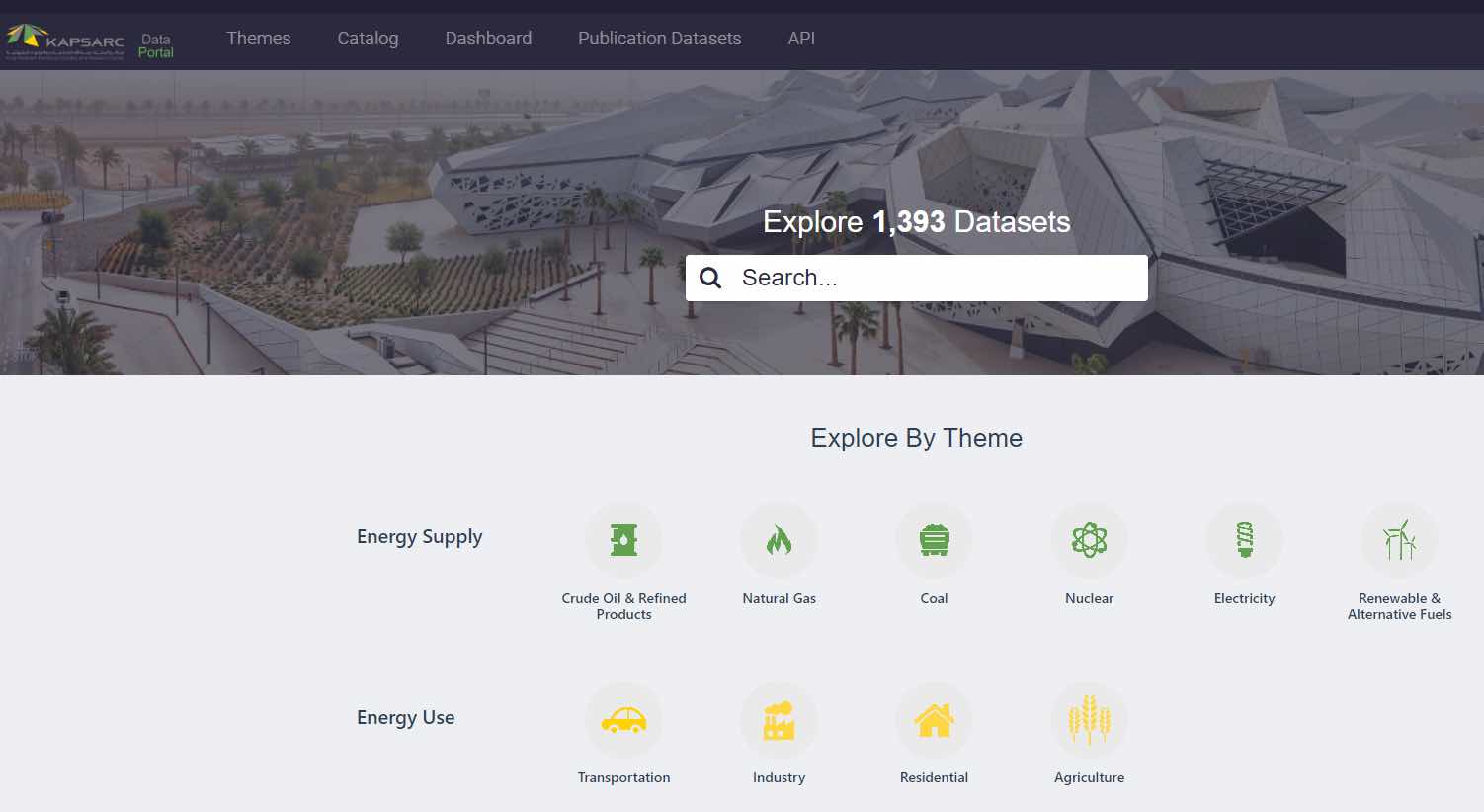
Saudi Arabian energy research center KAPSARC (the King Abdullah Petroleum Studies and Research Center) is building and extending a data culture outside the organization itself. While it started by making data on energy available internally to its 80 researchers, it has now opened its data to the world, and has nearly 1,400 datasets available on a wide range of energy topics.
The Smart Data Summit Plus on 16-17 November 2022 in Dubai will showcase the latest advances in data across the region and help organizations plan for the future. Opendatasoft will be attending to explain the importance of open data to the Middle East – come along to visit us at the Mövenpick Grand Al Bustan Hotel in Dubai to find out more.